Immunohistochemistry of Enamel Cell Proteins
High resolution images for teaching etc. are available on request
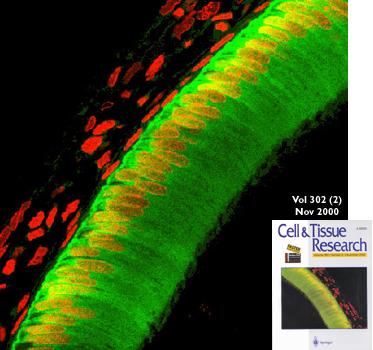
Calbindin-28kDa
 |
[Ref 7] |
Confocal microscopy of a cryosection of developing rat molar labelled with antibodies to calbindin-28kDa (a calcium-binding protein, digitally coded as green) and with the DNA stain propidium iodide (coded red). The principal enamel cells (ameloblasts) contain high levels of calbindin in the cytosol (green) and lesser amounts in nuclei (red/yellow). The accessory cells (upper left) lack calbindin so only their red nuclei are visible. In vivo, the black area at the top left would contain vascular connective tissue, and the black area at the bottom right would contain developing enamel and dentine.